Surface acoustic wave (SAW)-based acoustofluidics combines microfluidics with active microacoustic fields. This allows to realize numerous Lab-on-a-Chip operations, reaching from fluid manipulation including mixing, droplet and aerosol generation to the manipulation of cells and (bio-)particles.
SAW-based acoustofluidics & biomedicine
The sorting of specific cells and particles from complex body fluids, i.e. blood, is a critical step in personalized medicine and preparative diagnostics. Current methods reaching from density gradient centrifugation to size-exclusion chromatography are often carried out in a stepwise procedure combining different techniques. Future integrated solutions for handheld or PoC devices, however, require a technology for cell and particle fractionation without the need for sample pre- or posttreatment or cost intensive media, respectively, and with a high cell purity and recovery.
Surface acoustic wave (SAW)-based acoustofluidics is a promising technology to meet this demand, and devices with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannels have already demonstrated the ability to manipulate particles and cells. Still, the complexity in fabrication of microchannels on a wafer substrate is a current limit in order to mass produce chips for biomedical purposes.
Innovative acoustofluidic solutions by SAWLab Saxony
At SAWLab Saxony, the Competence and Application Center for Acoustoelectronic Fundamentals, Technologies and Devices, of the Leibniz IFW Dresden (www.SAWLab-Saxony.de) we developed a SAW-based acoustofluidic platform based on lithographically defined, on-chip integrated microfluidic channels to enable precise and reliable large-scale production [1, 2]. To fractionate biomedically relevant cells and particles from complex fluids, a chip layout with two stages with one interdigital transducer (IDT) pair each was designed.
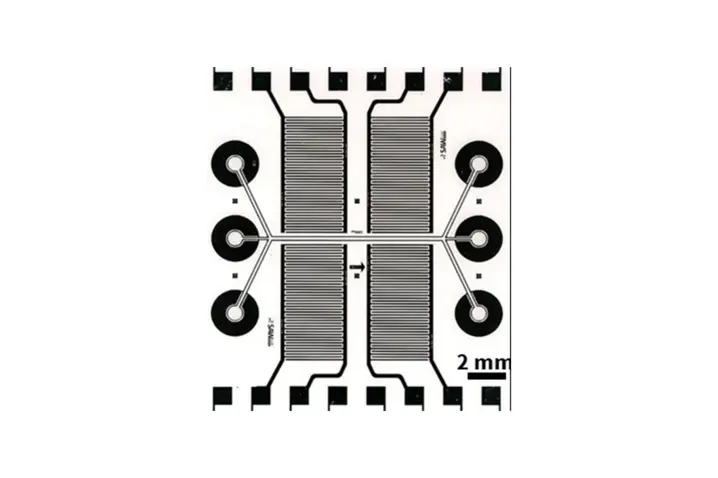
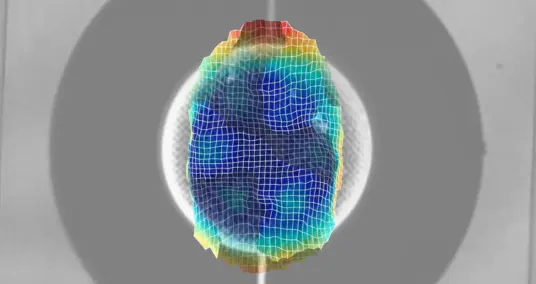
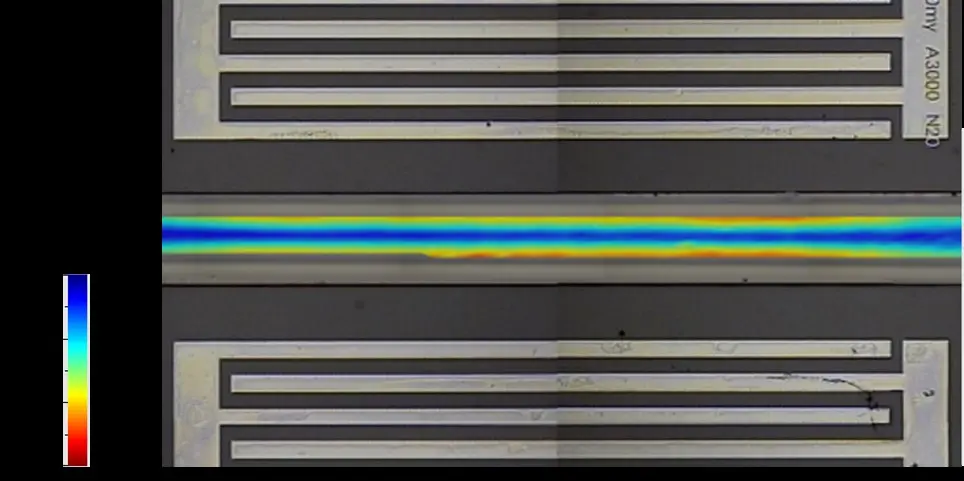
The acoustic field generated by these IDT pairs is driving a pressure gradient in the microchannel fluid by which cells can be influenced based on their intrinsic properties. First, the cells and particles are focused in the first stage and then separated from each other in the second stage due to different in size, density, shape or compressibility. The layout design was verified by measuring the SAW amplitude distribution in the open microchannel. For this purpose, a laser Doppler vibrometer (UHF 120, Polytec GmbH) was used (see Figure 2).
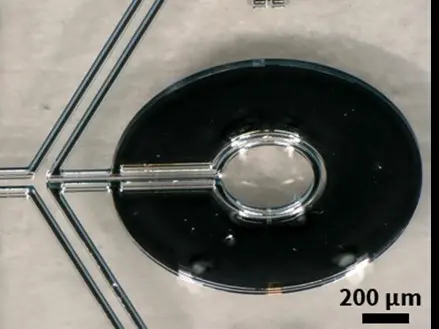
Blood cell sorting
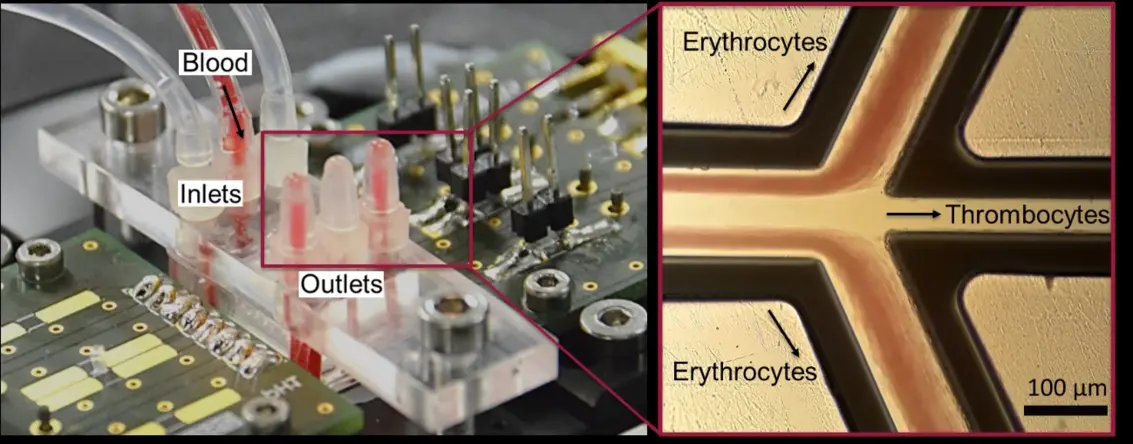
Using this chip type, we demonstrated the separation of blood components, i.e. the sorting of erythrocytes and thrombocytes (Figure 1)[3]. A model solution of erythrocytes and thrombocytes in whole blood concentration was supplied through the middle channel inlet. Additionally, a sheath flow was applied. First, all cells were focused in the center of the channel and then the larger erythrocytes were directed to the sides of the microchannel in the acoustic field. The erythrocytes could thus be collected and analyzed at the side outlets, the platelets at the middle one. In total, the platelets could be concentrated by a factor of 7.7 with a purity of 86% and a throughput of 45,000 cells/sec, respectively, making it the currently most advanced two-stage SAW-based thrombocyte sorting technology.
References
1. Winkler, A., et al., Compact SAWaerosol generator. Biomedical Microdevices, 2017. 19(1): p. 10.
2. Winkler, A., et al., SAW-based fluid atomization using mass-producible chip devices. Lab on a Chip, 2015. 15(18): p. 3793-3799.
3.Richard, C., et al., Blood platelet enrichment in mass-producible surface acoustic wave (SAW) driven microfluidic chips. Lab on a Chip, 2019. 19(24): p. 4043-4051.