The use of optical free-form surfaces allows complex lens systems to be simplified and thus made more compact and weight-optimized. In addition, the use of optical freeform surfaces enables the realization of completely new functionalities. At the same time, their manufacturing process is complex and therefore time-consuming and expensive. The production of individual freeforms in small batch sizes can be carried out efficiently using a CNC machine.
The Ernst Abbe University of Applied Sciences (EAH) Jena is working on optimizing the manufacturing process with the aim of making a prediction about the component surface quality based on vibration data recorded during surface processing and a direct evaluation using artificial intelligence. To this end, the influencing variables affecting the process chain are identified, quantified and optimized in such a way that the best possible production result is achieved.
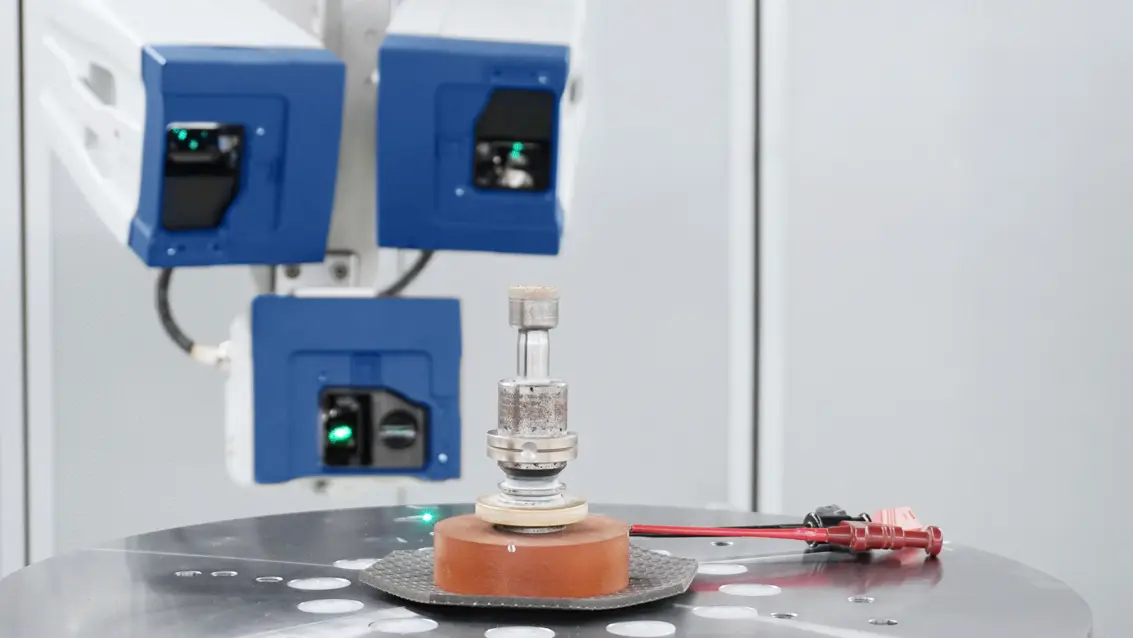
Influence of machine parameters on surface quality
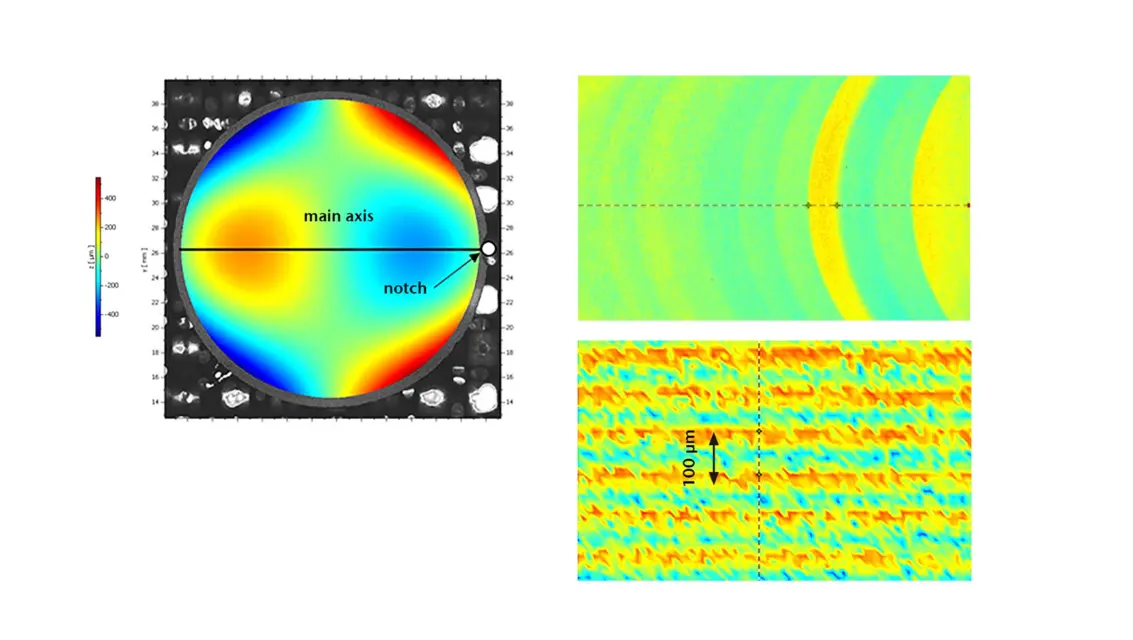
An optical free-form surface should not only have a high degree of dimensional accuracy, but also be free of short and medium-frequency surface defects, such as those caused by vibrations during the manufacturing process. The best possible surface quality is achieved by the final ultra-fine grinding process. However, the process chain from coarse grinding to fine grinding and ultra-fine grinding is subject to numerous influencing variables that affect the quality of the end product. In addition to the tool used and its alignment to the surface, process parameters such as speed, feed rate, infeed depth and the ultrasonic frequency used to excite the tool play an important role.
Only an optimal selection of all control variables leads to a surface that meets all the requirements for high-precision optics. In order to investigate the machine dynamics of the 5-axis CNC machine used to produce the flat-form surfaces by ultrasonic-assisted grinding and to identify the best possible machine setting, it is helpful to carry out a vibration analysis using laser Doppler vibrometry and to analyze the surface texture of the machined sample using white light interferometry.
Early prediction of surface quality using AI
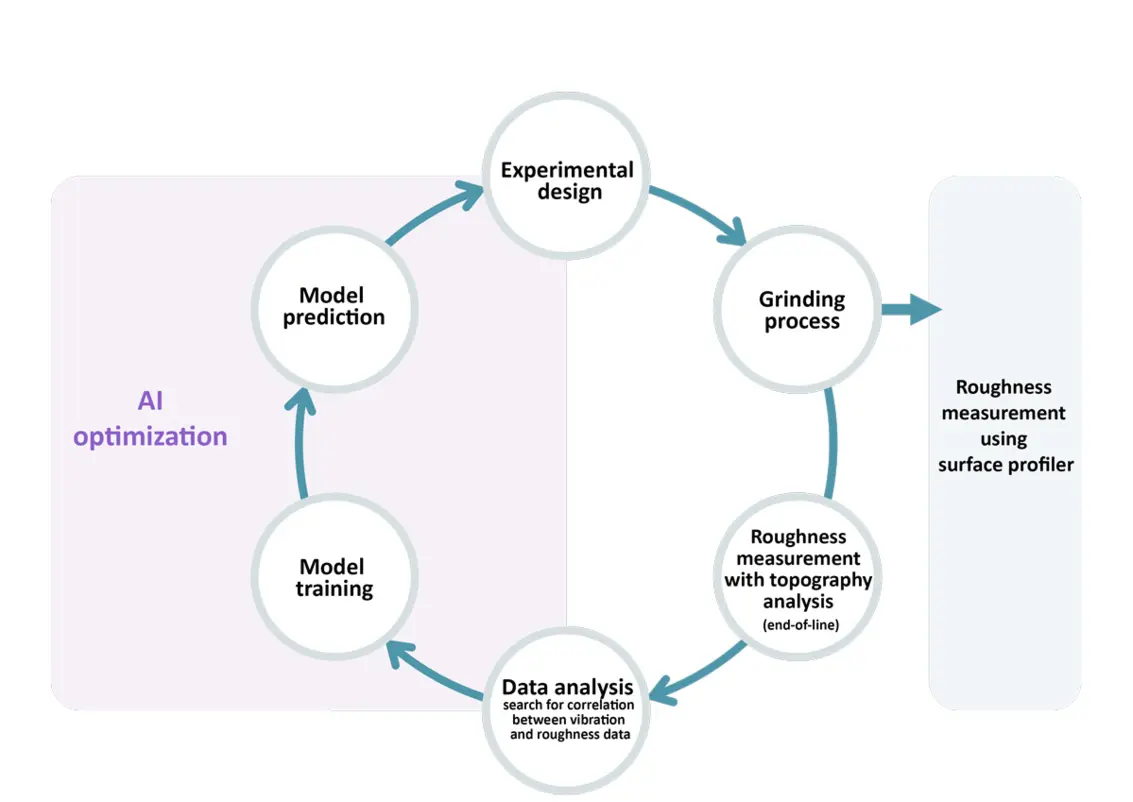
In order to be able to make a good statement about which machine parameters influence the final result and how, and to do this with the smallest possible number of test samples produced, support from artificial intelligence (AI) is helpful. In our case, we are using AI from Batix Software GmbH. They have developed a model to predict the surface quality, or the resulting roughness value of the surface based on machine parameters.
In a first step, the AI creates a test plan from the various available vibrometer data and surface parameters in order to identify the influencing machine parameters through the AI. The next step is to check how well the vibration analysis data correlates with the surface parameters of the white light interferometry.
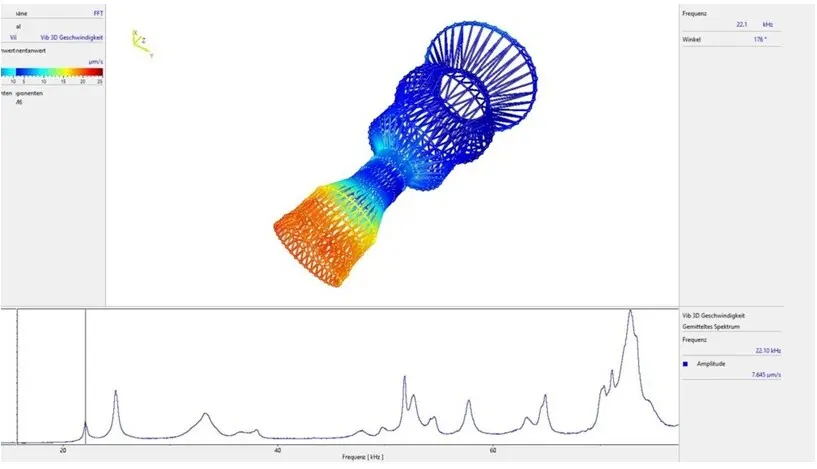
The influence of vibrations on surface quality
Vibration analysis is useful both when the machine is at a standstill and in operation. When the machine is at a standstill, the natural resonances of the machine components are determined by exciting various machine components with a modal hammer in order to prevent unfavorably selected tool speeds and ultrasonic frequencies from exciting the natural resonance frequencies of these components and leading to undesirable vibrations during the production process and thus negatively influencing the surface quality of the finished product.
During machine operation, vibration analyses can be carried out directly during workpiece processing. Non-contact vibrometers can also be used to measure the rotating tool during the operation of machine components. Non-contact measurements on the workpiece during operation are also possible. Such operating vibration analyses reveal effects that remain undetected when the machine is at a standstill.
For example, the temperature compensation built into the CNC machine causes steps of the order of 1 µm to form on the surface at intervals of one second. The distance between two steps is linked to the feed rate of the tool by the periodic repetition of the temperature compensation. As stated by the AI model, this leads to the important insight that the temperature compensation of the CNC machine can also be disadvantageous and may be better left switched off.
In order to investigate machine vibrations during workpiece machining and their effects on surface roughness, the laser beam used for optical vibration measurement is deflected in such a way that measurements can be taken directly on the underside of the workpiece during tool engagement. Detailed images of the surface structure were used to establish a direct correlation between the distance or spatial frequency of machining marks on the resulting workpiece surface and the grinding process parameters of speed and feed rate.
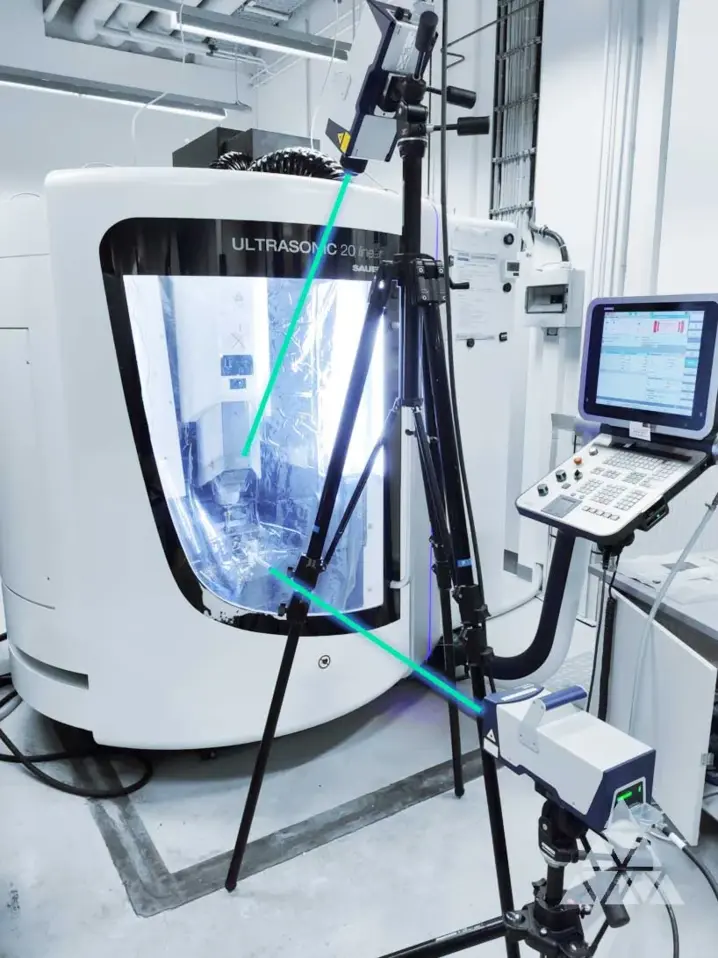

Prediction of surface quality using vibrometry and AI
The combination of the end-of-line surface measurement and the in-line vibration measurement data in a joint frequency display shows a high correlation between machine dynamics and the resulting surface structures.
The correlation of the optical vibration measurement with the optical surface measurement in combination with an AI made it possible to develop an understanding of the influencing variables of the grinding process parameters on the resulting surface quality.