Acoustofluidics is the active manipulation of fluids as well as of immersed particles or cells at the micro- and nanoscale and is a key technology for life sciences. Acoustic waves, more precisely, ultrasonic waves featuring high frequencies far beyond the audible range, are predestined for this purpose because they allow for precisely controllable and contact-free handling of very small objects. A novel mechanism for microfluidics driven by highfrequency acoustic waves has been developed at IFW’s SAWLab Saxony. The method is based on the active manipulation of the mechanical vibration plane of surface acoustic waves and was successfully demonstrated to significantly improve microfluidic actuation for lab-on-a-chip applications.
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices like high-frequency analog bandpass filters and resonators are already key components for all mobile communication devices, including wireless networks, mobile phones, Bluetooth and infrared signaling. The current activities at the SAWLab Saxony are focused on the second and third generation of SAW applications, namely I) wireless, self-sufficient sensing at high temperatures (>600°C) and harsh environments, and II) SAW-driven acoustofluidics.
The topic presented here refers to the latter one and results from a comprehensive approach considering electroacoustic fundamentals, functional thin films as well as the specific microfluidic application.
Polarization conversion of surface acoustic waves
Using ultrasonic waves for selective and noninvasive actuation of fluids as well as of immersed particles and cells at the microscale is state of the art. In general, the interaction of high-frequency mechanical waves with the fluid gives rise to acoustically induced forces that can be used for rapid fluid mixing, for sorting and trapping of particles/cells and for aerosol generation.
The most common method to excite ultrasonic waves relies on the inverse piezoelectric effect, i.e. the generation of mechanical strain in a specific solid material resulting from an applied electrical field. In case of surface acoustic waves (SAW), the voltage is applied to a pair of comb-shaped, planar electrodes (interdigital transducer, IDT) that are arranged on the piezoelectric substrate material, e.g. lithium niobate. Thus, the acoustic wave propagates along the substrate surface with a penetration depth in the order of the wavelength. The mechanical strain (displacement amplitude) is composed of three spatial components, namely, two in-plane components in parallel and perpendicular to the propagation direction respectively, as well as one out-of-plane component that is directed perpendicular to the surface. Moreover, an electrical field is accompanying the SAW since the mechanical strain generates an electrical potential due to the piezoelectric effect. The distribution of both, the components of mechanical displacement amplitude and the electrical potential represents the polarization of the surface acoustic wave.
SAW-based microfluidic devices mostly consist of at least one IDT on a piezoelectric substrate utilized for the excitation of high-frequency mechanical waves. The fluid and immersed particles/cells are in direct contact to the substrate surface and enclosed by a vessel commonly made from a polymer. For actuation purposes, vertically polarized SAWs are typically utilized due to their large out-of-plane (vertical) displacement amplitude that mainly provokes the transfer of momentum to the fluid resulting in the acoustic radiation force and acoustic streaming. Using vertically polarized SAW comes along with two major drawbacks:
I) the SAW is strongly attenuated during the transmission under the vessel wall and II) the interaction with the fluid immediately starts after the SAW encounters the fluid volume inside the vessel.
To overcome these drawbacks, an alternative approach has been invented and investigated at IFW’s SAWLab Saxony based on the selective conversion of SAW polarization. The fundamental idea is to excite a shear-horizontal SAW characterized by a dominating in-plane component of mechanical displacement that is directed perpendicular to the SAW propagation direction, and to change SAW polarization inside the microfluidic vessel in order to start fluid actuation (Fig. 2).
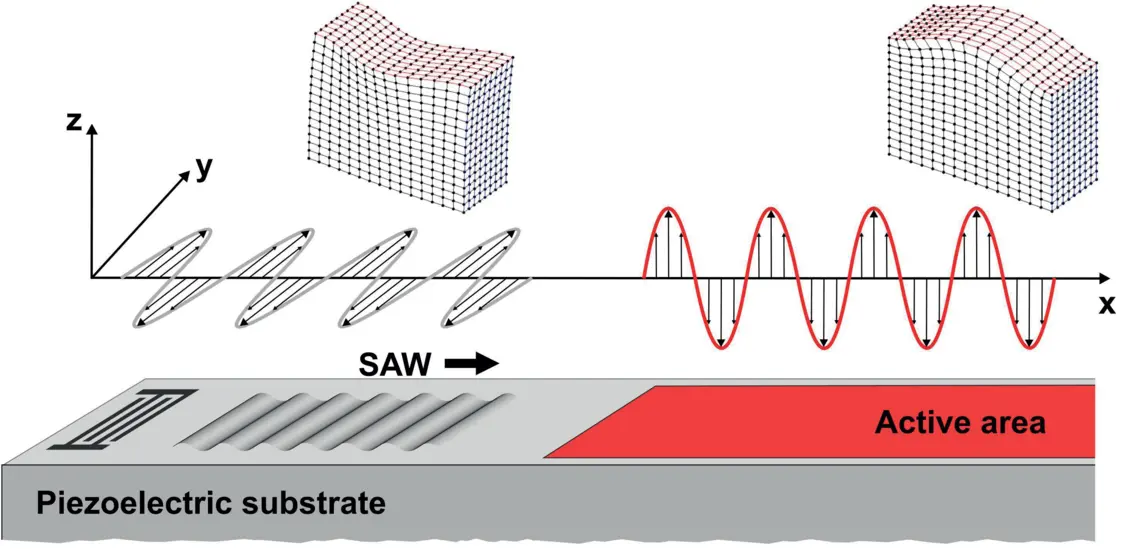
Using shear-horizontally polarized SAW significantly reduces the attenuation during transmission of the vessel wall. Moreover, the interaction with the fluid is minor as compared to vertically polarized SAW yielding almost no transfer of momentum. Thus, the outof-plane displacement has to be increased once the SAW propagates inside the vessel, i.e. the polarization has to be changed.
A straightforward approach for the selective conversion of SAW polarization has been investigated in the IFF research team Surface Dynamics. Therefore, a metal thin film is deposited on the surface of a piezoelectric substrate that locally changes the electrical boundary conditions of SAW propagation, i.e. shortens the electrical field at the substrate surface. Under certain conditions, i.e. for particular substrate materials, the out-of-plane displacement amplitude significantly increases if the SAW passes the transition from free to metallized surface. This effect was comprehensively investigated with the help of experiments and simulations.
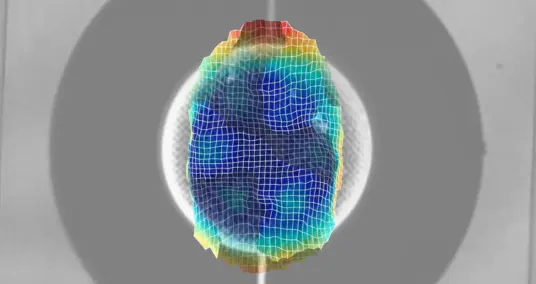
A high-frequency laser Doppler vibrometer was used to realize high-resolution measurement of the out-of-plane (vertical) component of mechanical displacement. Corresponding results also help to validate numerical simulations and the underlying physical model. Performing simulations is of particular importance because it gains insight to micro acoustic fundamentals that are not accessible by means of experiment, e.g. the determination of the complete SAW polarization vector as well as the detection of other acoustic wave modes inside the substrate material.
New opportunities for SAW-driven microfluidics
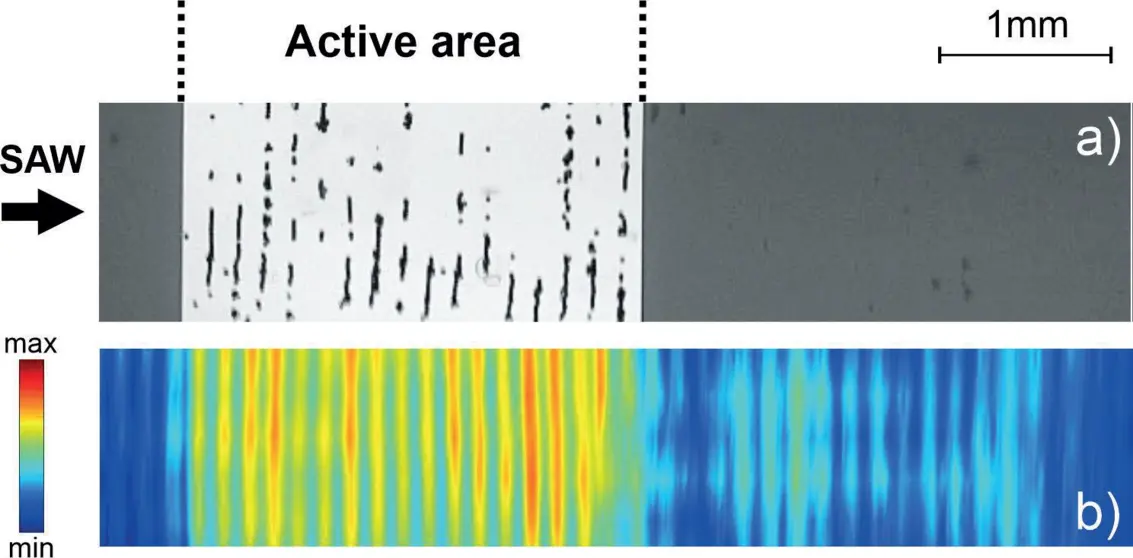
The novel concept of SAW polarization conversion provides two main advantages for microfluidic actuation purposes. Besides the reduced attenuation of SAW during transmission of the vessel wall, the region of fluid actuation (active area) can be precisely selected by means of the lateral layout of the metallized substrate area. This effect was successfully demonstrated for the trapping of particles (10 µm diameter) immersed in water (Fig. 3). The particles accumulate within the active area characterized by a larger out-of-plane displacement amplitude caused by the intended change of SAW polarization. Thus, the acoustic radiation force induced by the vertical displacement is significantly higher at this region yielding to a trapping of particles. Regions without this polarization conversion show significantly lower amplitudes yielding minor forces in the fluid not capable to trap particles.
The lateral position, the dimensions as well as the shape of the active area can be simply adapted by means of the lateral layout of the metal thin film. Hence, a new degree of freedom is available for the design of SAW-driven microfluidic devices that are predestined for controllable handling, e.g. separation or trapping of cells.
The fundamental concept of SAW polarization conversion has been granted as a patent (DE 10 2017 118 878).
References
[1] A.N. Darinskii et al., Ultrasonics 78 (2017) 10
[2] A.N. Darinskii et al., J. Appl. Phys. 123 (2018) 014902
[3] R. Weser et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 117 (2020) 143502
*With kind permission of the Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden e. V.: This article is an authorized reprint from the IFW Annual Report 2020.